News
better business decisions
Posted 5 months ago | 5 minute read

The Capacity Market: everything you need to know
The Capacity Market prequalification window is now open.
The Capacity Market in the UK is a mechanism designed to ensure the security of the electricity supply by guaranteeing sufficient capacity to meet demand, particularly during peak times. It achieves this by paying generators, demand-side response providers, and energy storage operators for making capacity available when needed.
Capacity Market Agreements (CMAs) are contracts awarded through competitive auctions that commit participants to provide a set volume of capacity when called upon, in return for regular payments.
The prequalification window runs from 9am on 5 August to 5pm on 30 September, for companies looking to access this revenue stream prequalification is a requirement. In this article, we explore what the Capacity Market is, why it’s needed, and how you can participate.
What is the Capacity Market?
The UK’s electricity system is undergoing significant change, with more intermittent renewable generation, ageing infrastructure, and fluctuating demand patterns. The Capacity Market provides a safety net, ensuring there is always enough reliable capacity available to meet peak demand, particularly during winter evenings when electricity use is highest.
Launched in 2014, the Capacity Market is a government-backed mechanism designed to ensure that electricity supply meet demand by offering payments to providers who commit to making their capacity available at short notice. Participants are paid based on their ‘de-rated’ capacity, which is calculated by multiplying their nameplate capacity by a technology specific de-rating factor.
Unlike wholesale power markets, the Capacity Market exists as a separate scheme, with its own rules written into UK legislation. Auction parameters, such as total capacity to procure and the cap on bid prices, are set annually by the UK’s Secretary of State for Energy Security and Net Zero.
Who can participate?
The Capacity Market is a technology-neutral mechanism in which most types of capacity can participate, including:
- new and existing on- or offshore generation plant (all types of generation plant including combined heat and power (CHP))
- storage
- demand-side response (DSR)
- interconnector capacity
The following forms of capacity are not eligible to participate in the Capacity Market:
- capacity receiving low carbon support (e.g. through the Renewables Obligation, Contracts for Difference, or small-scale Feed in Tariffs (FIT))
- capacity with long-term contracts to provide Short-Term Operating Reserve (STOR) unless an irrevocable declaration is made to terminate the STOR contracts if awarded a capacity agreement
The Capacity Market auction is a descending clock or reverse auction. This means that prices start high, with everyone participating in the auction. Every round, the price decreases. Participants can submit an Exit Bid when the price is too low for them. Once the capacity left in the auction is lower than the target capacity, the auction clears. Everyone left in the auction receives the same price (pay-as-clear).
Two main types of auctions are held:
- T-4 auctions: held four years ahead of the delivery year to secure the majority of the required capacity
- T-1 auctions: held one year ahead to fine-tune capacity needs, covering any gaps in the market
Before participating in a Capacity Auction, companies need to Prequalify the resources for which they are seeking Capacity Agreements. The EMR Delivery Body, which managed the Capacity Market, uses the information submitted during Prequalification to verify that generation and DSR Capacity Market Units (CMUs) are eligible to participate in the Auction and to establish the capacity of individual CMUs. The Prequalification process also enables licensed owners of existing licensable generation units to notify their intention to Opt-out of a Capacity Auction should they not wish to enter.
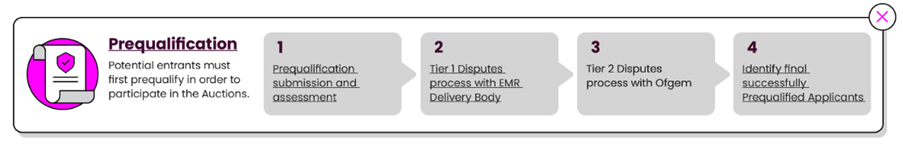
Source: NESO
How does it work?
The Capacity Market pays for availability, not actual generation. This means participants are rewarded for being ready to deliver electricity or reduce demand if required, even if they are not ultimately called upon.
The mechanism is only triggered during stress events. These are extreme situations when electricity supply is tight. During these events
- the National Energy System Operator (NESO) issues a Capacity Market Notice (CMN) to warn participants up to four hours before a potential shortage
- If the notice is not cancelled and NESO takes demand-control action, a stress event is confirmed
- Capacity Providers must deliver the contracted capacity volume or face penalties for underperformance
How GridBeyond can help
- Auction participation: our experts oversee the entire auction process, from registration through to final bidding, ensuring your assets achieve the most competitive agreements available
- Satisfactory Performance Days (SPDs): we work closely with customers to help them meet their capacity commitments by achieving SPDs and confirming asset performance during periods of critical system demand
- Maximising revenue: taking part in the Capacity Market does not always limit your ability to generate revenue from other flexibility services. We ensure your assets can benefit from the Capacity Market while also participating in additional income-generating opportunities
- Asset assessment and preparation: we prepare and qualify a diverse range of assets for Capacity Market participation, including both new and existing generators, flexible loads, and energy storage systems. This includes verifying metering configurations to ensure they meet all compliance standards
- Connection and operational integration: your assets are integrated with our 24/7 Network Operations Centre (NOC) via API or hardware, allowing for continuous communication and real-time data transfer. When a Capacity Market Notice is issued, our operators work directly with your site to ensure assets are ready and able to respond
- Contract support: we support businesses with Capacity Market Agreements throughout the full term of their contracts. Using advanced data analytics and intelligent scheduling, we help ensure performance obligations are met. If operational circumstances change and a site cannot fulfil its commitment, our Secondary Trading Clearing House enables the buying or selling of capacity obligations with other qualified participants. This reduces the risk of penalties and provides flexibility to adapt to changing conditions
Whether you are a new entrant seeking prequalification or an established participant aiming to enhance performance and manage trading, GridBeyond delivers the expertise, tools, and market insight needed to succeed in the Capacity Market.