News
better business decisions
Posted 6 months ago | 4 minute read

US grid reliability and security at risk, warns DOE
The US Department of Energy (DOE) has released a report noting that existing generation retirements and delays in adding new firm capacity could lead to a rise in power outages and a growing mismatch between electricity demand and supply.
The Report on Evaluating U.S. Grid Reliability and Security, published on July 7 fulfills Section 3(b) of President Trump’s Executive Order, Strengthening The Reliability And Security Of The United States Electric Grid, by delivering a uniform methodology to identify at-risk regions and guide Federal reliability interventions.
The report estimates an additional 100GW of new peak hour supply is needed by 2030. Of this, 50GW of this is directly attributable to data centers. It claims that if current generator retirement schedules and incremental additions remain unchanged, most regions will face “unacceptable reliability risks” within five years and the Nation’s electrical power grid will be unable to meet expected demand for AI, data centers, manufacturing and industrialization. With projected load growth, retirements increase the risk of power outages by 100 times in 2030 and annual outage hours could increase from single digits today to more than 800 hours per year.
All regions except ERCOT currently have less than 2.4 hours of average loss of load per year, ERCOT would be expected to experience on average 3.8 hours of average loss of load per year. But the report warned that allowing 104GW of firm generation to retire by 2030, without timely replacement, could lead to significant outages when weather conditions do not accommodate wind and solar generation. The DOE assumes 104GW of announced plant closures by 2030 will be met with 210GW of new generation; however, only 22GW of that new generation will be firm, reliable, dispatchable generation. As a result the outage risk in several regions rises more than 30-fold with average loss of load per year ranging from 7 hours/year in CAISO to 430 hours/year in PJM.
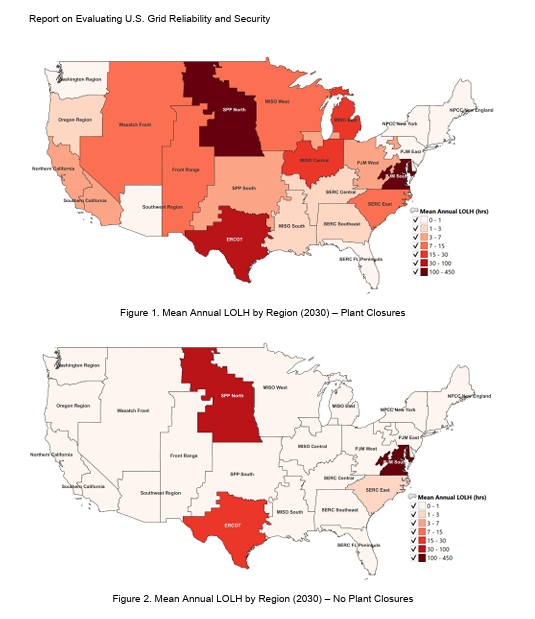
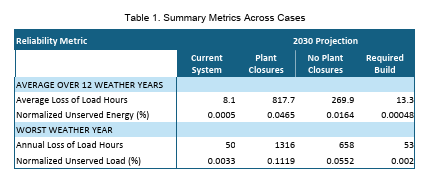
Source: DOE
The report also notes that traditional peak-hour tests used to evaluate resource adequacy do not sufficiently account for growing dependence on neighboring grids. It said that methods to evaluate resource adequacy also need to incorporate frequency, magnitude, and duration of power outages, and move beyond exclusively analyzing peak load time periods, and develop integrated models to enable proper analysis of increasing reliance on neighboring grids.
A powerful solution
On-site battery energy storage has emerged as a powerful and strategic solution for businesses facing grid reliability concerns. By storing electricity on-site, businesses are no longer solely dependent on the grid for uninterrupted power. Instead, they gain a resilient, flexible energy asset that can be used not just for backup power, but also to optimize energy use, lower operational costs, and contribute to sustainability goals.
One of the most immediate and tangible benefits of battery energy storage is its ability to avoid the financial losses associated with unplanned outages. During a grid failure, a battery system can provide electricity to critical systems or even the entire site, maintaining production lines, data operations, refrigeration, and safety infrastructure.
Another key advantage is resilience against voltage fluctuations and power quality issues, which can be just as damaging as full outages. For operations involving sensitive equipment, automated manufacturing, or continuous processes, even brief disturbances can cause malfunctions, product defects, or restarts that cost time and money. A battery system can act as a buffer, smoothing out irregularities in the incoming power and ensuring a clean, stable supply.
Beyond this, batteries can be used for peak shaving, which involves discharging stored energy during times of high grid demand when electricity prices spike. By reducing a facility’s peak demand charges, which often make up a significant portion of commercial energy bills, businesses can achieve substantial cost savings. Batteries also provide an opportunity to participate in services like frequency response, load shifting, or reserve capacity. Battery storage enables companies to tap into these revenue streams by intelligently charging and discharging energy when the grid needs support.
Battery storage also supports decarbonization and sustainability efforts. When paired with on-site renewable generation such as solar PV, batteries allow businesses to store excess renewable energy for later use, reducing dependence on grid power. This not only lowers emissions but also strengthens energy autonomy and shields against future energy price volatility.
Ready to protect your business?
For businesses where energy equals output power supply protection is critical. Investing in an on-site battery can help your business avoid costly disruptions, enhance sustainability, and unlock new revenue streams, all while gaining a competitive edge in a power-constrained world.
If you’re considering on-site battery storage or want to learn more about how to reduce your energy risk, contact us today for a free energy resilience assessment.

CaPex-Free Battery | Resilience, carbon reduction and revenue
Our AI-powered platform, ensures that full power resilience is delivered instantaneously, preventing disruption to even the most sensitive equipment.
Learn more


